Did you know that oleuropein—the mighty polyphenol found in humble olive leaves and olive oil—may be a driving force behind the Mediterranean diet’s ability to add years to your life? Surprising studies suggest that this little-known compound is responsible for much of the heart-health, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory protection Mediterranean cultures enjoy. So, what’s the real story behind this olive-derived secret? Dive in, and you’ll discover why experts and avid health seekers alike are making space for oleuropein in their daily routines.
Oleuropein: A Surprising Powerhouse—Did You Know?
Opening Hook: The Startling Truth Behind Oleuropein’s Popularity
Think olive oil is healthy just because it’s “good fat”? There’s more behind its reputation—and it starts with oleuropein. Scientists have discovered that this phenolic compound, abundant in olive leaves and extra virgin olive oil, can influence cell lines associated with cancer, help lower blood pressure, and dramatically reduce the risk of heart disease. Research is mounting around the protective effects of oleuropein, explaining why olive-centric diets top the charts for longevity. As the world searches for natural solutions to modern health challenges, oleuropein has soared in popularity—transforming the way people view not just olive oil, but the entire olive tree and its related products. If your goal is stronger immunity or to shield your body from oxidative stress, this Mediterranean marvel should be on your radar.

What You’ll Learn About Oleuropein
- The science and origins of oleuropein
- How oleuropein fits into the Mediterranean diet and lifestyle
- The health benefits and protective effects of olive leaves and olive oil
- Why olive leaf extract is generating buzz
- FAQs about oleuropein, dosages, and safety
Understanding Oleuropein and Its Origins
The Chemistry of Oleuropein: What Makes It Unique?
Oleuropein is a phenolic compound found predominantly in the olive tree (Olea europaea). What gives it such a revered status among scientists and nutritionists? Its unique chemical structure—comprised of a phenolic core blend of elenolic acid and hydroxytyrosol linked by an ester bond—sets it apart even among other beneficial olive phenols. This configuration gives oleuropein a bitter taste and a range of health-promoting actions, including potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help neutralize free radicals and lower oxidative stress in cell lines. Ultramodern research continues to uncover how oleuropein’s chemical arrangement enables these beneficial effects, distinguishing it as a standout in both olive leaf and virgin olive oil, and making it a focus for functional foods and supplements.
Not only is the concentration of oleuropein highest in fresh olive leaves, but it is also found in lesser amounts in unripe olives and cold-pressed olive oils. When you consume extra virgin olive oil or olive leaf extract, you’re benefiting from these active molecules at their most bioavailable. Ongoing studies on cancer cell and breast cancer cell lines show promising protective effects, giving oleuropein significant attention from researchers exploring new ways to combat disease and support overall wellness through diet.
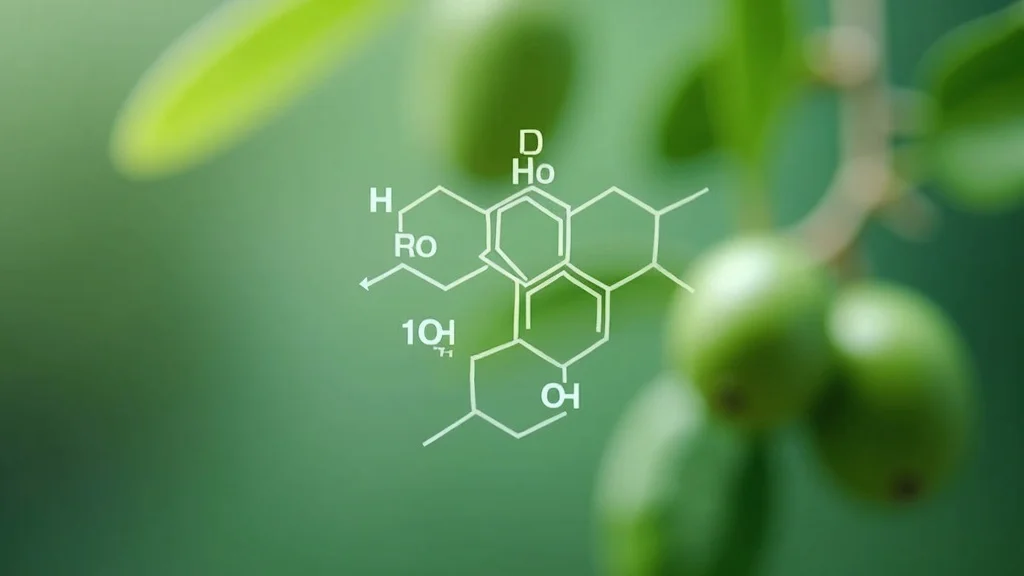
Oleuropein in Olive Tree, Olive Leaves, and Olive Oil—A Brief Overview
Oleuropein is deeply woven into the life cycle of the olive tree, with its highest levels in young, fresh leaves and immature olives. While the olive leaf is traditionally used in teas and extracts—boasting a slightly astringent, green flavor—oleuropein is also distributed throughout quality olive oil, especially extra virgin olive oil. As olives ripen, oleuropein content decreases, which explains why fresh olive products often taste more bitter than their mature, brined, or processed counterparts.
“The secret to the Mediterranean diet’s long-term health benefits has always been rooted in oleuropein-rich foods.”—Prominent Nutritionist
These natural concentrations mean that Mediterranean diets, rich in olive-based foods, maintain a consistent intake of oleuropein and its derivatives. Olive leaf extract, in particular, offers a potent form for those seeking therapeutic levels. Regardless of whether it comes from olive oil, olive leaves, or the olive tree itself, oleuropein is foundational to the protective effects associated with Mediterranean eating patterns and stands out among other phenolic compounds for its broad health reach.
Health Benefits of Oleuropein

How Oleuropein Contributes to the Mediterranean Diet
Followers of the Mediterranean diet have long enjoyed some of the world’s highest life expectancies and lowest rates of chronic illnesses. A significant reason for this is their daily inclusion of olive-based foods—infusing their meals with concentrated doses of oleuropein. This compound is known for supporting cardiovascular health, lowering bad cholesterol, and reducing blood pressure, particularly in populations who consume extra virgin olive oil and olive leaf extract regularly.
It’s not just about the oil; the whole ecosystem—olives, olive leaves, and olive-based teas—delivers a synergy of phenolic antioxidants. Clinical evidence suggests the intake of oleuropein-rich foods helps regulate oxidative stress, enhance the balance of good and bad cholesterol, and modulate inflammation. This underpins the protective effect observed against degenerative diseases, with the beneficial impact observed in cell lines exposed to Mediterranean dietary patterns. Because of this, healthcare professionals increasingly recommend incorporating authentic olive oil and olive lea-based products into daily diets for their broad spectrum of health benefits.
Interestingly, the way natural compounds like oleuropein interact with our bodies is similar to how certain simple ingredient combinations can deliver powerful results in other wellness areas. For example, if you're curious about how minimal, natural formulas can be highly effective, you might find it eye-opening to explore the science behind the best teeth whitening formula using just two ingredients—a testament to the potency of nature’s simplicity.
Exploring the Protective Effects of Oleuropein: Scientific Evidence
What makes oleuropein more than just a healthy-sounding trend? The science is compelling. Multiple studies have demonstrated that oleuropein, when introduced to cancer cells and breast cancer cell lines, can inhibit proliferation and trigger protective mechanisms. Its antioxidant effects support cell health by reducing markers of oxidative stress—a known contributor to heart disease, cancer, and premature aging. Notably, research published in leading journals highlights the protective effect of oleuropein in reducing inflammation and improving vascular health, helping lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Beyond its influence on cells, oleuropein is also credited with bolstering immune response and modulating sugar metabolism, potentially benefiting those at risk of metabolic disorders. It is this wide-ranging scientific backing that cements oleuropein’s spot as a core compound sustaining the positive reputation of olive oil and olive leaf extract globally. Whether you’re seeking support for heart health, immune function, or longevity, the protective effects of this polyphenol deserve your full attention.
Oleuropein in Olive Leaf Extract: An Overlooked Gem
While extra virgin olive oil gets the spotlight in discussions about the Mediterranean diet, olive leaf extract is where the true concentration of oleuropein can be found. A favorite among wellness enthusiasts, olive leaf extract delivers up to 20 times the oleuropein content of the same volume of olive oil—making it a potent ally for those pursuing the maximum effects of oleuropein.
This extract is growing in popularity for its immune-support features and its ability to deliver consistent dosages. Whether used as a supplement or brewed as a tea, olive leaf extract provides an easy, efficient way to capitalize on the benefits confirmed by decades of traditional Mediterranean practice and verified by modern cell line and clinical studies. With low reported side effects, it’s no wonder olive leaf extract is hailed among functional foods as “the overlooked gem” of the olive tree.

| Health Benefit | Oleuropein Source | Supporting Study |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular protection | Olive oil, olive leaves | European Food Safety Journal |
| Antioxidant support | Olive leaf extract | Journal of Nutrition |
| Immune modulation | Olive tree | Phytomedicine Review |
Oleuropein vs. Other Phenolic Compounds in Olive Oil

- Comparing health benefits: Oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and other phenols
- Why oleuropein stands out in olive lea and olive leaf
Olive oil has a reputation for being packed with powerful antioxidants, but a closer look reveals oleuropein has the edge over most other phenolic compounds. Take hydroxytyrosol—another Mediterranean darling with well-established antioxidant effects—it’s derived from oleuropein as olives mature. While both contribute to heart and cellular health, studies reveal oleuropein exerts broader protective actions, including the ability to modulate immune response and influence cell lines linked to serious diseases. What truly sets oleuropein apart is its prevalence in olive lea and olive leaf, making tea, extracts, and supplements particularly effective for targeting specific health goals. The evidence lines up that not all olive phenols are created equal; for the full Mediterranean benefit, focus on maximizing your intake of oleuropein from diverse olive sources.
The Powerful Effects of Oleuropein: Real Stories & Case Studies
“After incorporating olive leaf extract in my routine, my yearly bloodwork has never looked better.” —Active User
Behind the headlines and research studies are real people experiencing the tangible benefits of incorporating more oleuropein into their diets. Case studies consistently show improved cardiovascular health metrics, such as lower blood pressure and cholesterol, among those routinely consuming olive leaf extract or increasing their intake of high-quality virgin olive oil. Anecdotes abound of Mediterranean locals enjoying long, active lives—often attributed to the natural, daily presence of oleuropein in their meals. Even individuals diagnosed with high risk for metabolic syndromes find support in science-backed dietary strategies that prioritize oleuropein-rich foods, lending evidence to its often celebrated, but underappreciated, role in Mediterranean wellness.
From improved bloodwork to decreased inflammation markers and a general boost in energy, the lived experience of users aligns well with existing research. When people switch to diets brimming with olive leaf, olive lea, or high-quality olive oil, myriad positive effects often follow—reinforcing oleuropein’s rank as a true wellness powerhouse.
How To Add More Oleuropein to Your Diet
Oleuropein in Everyday Foods: Practical Tips

- Choosing the right olive oil
- Olive leaf teas: preparation and taste
- Supplements: Olive leaf extract capsules
Bringing more oleuropein into your daily routine doesn’t require a major lifestyle revamp. Opt for extra virgin olive oil, which retains the highest levels of phenolic compounds—or better yet, go for “cold-pressed, early harvest” varieties known for their elevated oleuropein content (though their bitter taste signals a richer polyphenol profile). Add a drizzle of this oil to salads or grilled vegetables, or finish warm dishes just before serving to maximize health benefits.
Another easy strategy is incorporating olive leaf tea—simply steep dried olive leaves (found in health stores or online) in hot water for 10 minutes, then enjoy as an earthy, green, slightly tannic beverage. For targeted support, consider olive leaf extract supplements, which allow you to standardize your oleuropein intake without consuming large amounts of oil. Whether you’re seeking the pure form from the olive lea or supplementing via capsules, these approaches ensure you benefit from the full protective effect without unnecessary calories.
Oleuropein: Is It Safe?

Potential Risks, Dosages, and Who Should Avoid Olive Leaf Extract
Oleuropein from olive leaf extract and olive oil is generally considered safe for adults when consumed in amounts commonly found in foods or reputable supplements. As with any active herbal ingredient, moderation and proper dosing are essential, as high concentrations can sometimes lead to mild side effects like digestive discomfort. People with allergies to olive products should avoid supplements, and those taking medications for lower blood pressure or diabetes should consult their healthcare provider, as oleuropein may enhance the effects of these drugs. Likewise, children, pregnant women, or people on complex medical regimens should consult a healthcare professional before starting olive leaf extract.
In rare cases, allergic responses have been reported. Choose supplements from reputable sources for accurate dosing and product purity. Responsible use minimizes side effects, ensuring most adults can safely enjoy the benefits of oleuropein as part of a Mediterranean-inspired diet.
Mythbusting: Is Oleuropein Poisonous?

There’s a common myth that oleuropein, especially in concentrated forms like olive leaf extract, is toxic. Scientific reviews and global food safety authorities confirm that both dietary and supplemental forms are broadly safe when used appropriately. The naturally bitter flavor of fresh olive products is simply a marker of healthy oleuropein levels—not a warning sign of toxicity.
Serious side effects or toxicity are extremely rare and usually linked to excessive, unregulated supplement intake. Consuming oleuropein through typical Mediterranean diet foods or as directed supplement dosages is a safe, evidence-based way to unlock its benefits without risk.
| Concern | Scientific Consensus | Source |
|---|---|---|
| General safety | Safe for adults | EFSA, 2022 |
| High concentrations | Monitor dose | JAMA |
| Allergic responses | Rare | Mayo Clinic |
People Also Ask
What is oleuropein good for?
Oleuropein is well-studied for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which help protect heart and vascular health, support immune response, and modulate cholesterol and blood sugar metabolism. Research shows it can help lower blood pressure, reduce oxidative stress, and exert protective effects on cells, particularly in the context of inflammation and chronic disease prevention. Some studies even highlight its potential for impeding the growth of cancer cells and offering support in diabetes management. Both traditional and clinical evidence confirm that oleuropein is a cornerstone of the health benefits attributed to olive-based diets and supplements.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Oleuropein and Related Olive Compounds

Modern scientific analysis confirms the effects of oleuropein are wide-reaching, from protecting cell lines against damage to lowering cardiovascular risk and slowing oxidative stress. Studies with olive leaf extract, extra virgin olive oil, and pure oleuropein consistently report beneficial outcomes in cholesterol profiles, insulin sensitivity, and immune system modulation. Laboratory trials on cancer cell and breast cancer cell lines demonstrate oleuropein’s influence on metabolic and inflammatory pathways—key factors in disease prevention. Such evidence cements oleuropein’s reputation as the “active heart” of the Mediterranean diet’s longevity magic.
What foods are high in oleuropein?
Foods naturally high in oleuropein include fresh olive leaves, table olives (especially unripe or less-processed varieties), and extra virgin olive oil harvested early in the season. Specialty items like olive leaf tea and olive leaf extract capsules provide concentrated oleuropein in a convenient format. For those seeking optimal health benefits, focus on cold-pressed, early-harvest virgin olive oil and consider augmenting with olive lea-based products or supplements.
Top Dietary Sources: Olive Leaf, Olive Oil, and Table Olives

The best oleuropein sources are the leaves and fruit from the olive tree. Olive leaves can be dried for tea or extracted into concentrated supplements. Unripe table olives (often green or purple) and extra virgin olive oil are rich in the compound, especially when produced with minimal refining. Look for oils labeled “extra virgin” and with harvest dates for assurance of maximum phenolic content.
Who should not take olive leaf extract?
Although most adults tolerate olive leaf extract well, some individuals should avoid it or seek medical guidance before use. If you have allergies to olives or pollen from the olive tree, have chronic kidney issues, or take medications for blood pressure or diabetes, consult your doctor, as the supplement may interact or enhance the effects of these drugs. Children, pregnant women, and anyone with autoimmune or complex medical issues should avoid self-medicating with high-dose olive leaf extract.
Special Populations and Potential Adverse Effects
Vulnerable groups—including those with known plant allergies, children, pregnant listeners, and individuals with existing renal or blood pressure conditions—should exercise caution. Mild side effects are possible, such as gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions, but severe events are rare. If in doubt, stick with food-based sources of oleuropein or discuss supplement strategies with your healthcare provider.
Is oleuropein poisonous?
Ingesting oleuropein through typical food sources, including olive oil, olives, or leaf tea, is safe and provides wide-ranging health benefits. Only when consumed in extremely high, unregulated doses (not typical of food or commercial supplements) would toxicity potentially become a concern. Stick to recommended doses and choose products from reputable providers for peace of mind.
Current Research on Oleuropein Toxicity and Safe Usage
Current research indicates a high degree of safety for oleuropein in both dietary and supplemental forms, with toxicity virtually nonexistent at everyday or clinically recommended levels. Studies on olive leaf extract confirm no proven hazard when following established guidelines; most concerns revolve around proper dosage, occasional rare allergies, and interactions with certain medications. Reviews in pharmacology consistently affirm the compound’s safety for well-informed, responsible use.
FAQs on Oleuropein, Olive Leaf Extract, and Olive Oil
How does oleuropein differ from hydroxytyrosol?

Oleuropein is a core phenolic compound found in olive leaves and unripe olives, and it’s primarily responsible for their distinctive bitter taste and health-promoting actions. Hydroxytyrosol, on the other hand, is a breakdown product of oleuropein generated during the ripening of olives or the processing of olive products. While both are strong antioxidants, oleuropein’s structure allows for a broader range of protective effects—most notably in immune response and metabolic regulation. Hydroxytyrosol shines as a more targeted antioxidant, but oleuropein dominates in whole-plant and extract-based products for its multi-system wellness capabilities.
Can oleuropein supplements replace olive oil in the diet?
While olive leaf extract supplements offer a concentrated, standardized dose of oleuropein, they don’t replicate the complete nutritional profile of olive oil—which contains heart-healthy fats, vitamin E, and other bioactive phenols that act in concert for optimal health. For true Mediterranean diet benefits, combine supplements with regular, moderate intake of extra virgin olive oil and olives for both oleuropein and whole-food nutrition.
Does cooking affect the content of oleuropein in olive oil?
Yes, heat can degrade oleuropein and related polyphenols in olive oil, especially with prolonged cooking. For the highest oleuropein content, use extra virgin olive oil as a finishing drizzle or mix into uncooked dishes. Reserve high-quality oils for salads, dips, or last-minute garnishes—while olive lea and leaf extract (tea or capsule) are heat-stable alternatives for supplements.
Key Insights on Oleuropein Revealed
- Oleuropein’s broad health benefits are rooted in Mediterranean diet traditions
- Most olive-based foods owe much of their health impact to oleuropein and related phenols
- Proper dosing and selecting reputable sources are important for safety
Final Thoughts: Why Oleuropein Deserves a Place in Your Wellness Routine
Summing Up: The Lasting Magic of Oleuropein in Olive Oil and Olive Leaf Extract
Oleuropein is the Mediterranean’s best-kept secret—a scientifically proven champion for heart, immune, and overall health. Experience its magic by making olive lea, olive leaf, and high-quality olive oil staples in your daily routine, while keeping advice on safety and quality in mind. Your wellness journey never tasted better.
If you’re inspired by the transformative power of natural compounds like oleuropein, there’s a world of simple, science-backed wellness strategies waiting to be discovered. Exploring how everyday ingredients can deliver outsized benefits is a smart next step on your health journey. For instance, uncovering the secrets behind effective, minimalist approaches—such as the best teeth whitening formula made from just two ingredients—can open your eyes to the potential of nature’s most accessible solutions. Continue your exploration and empower your routine with insights that make healthy living both easy and effective.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment